ขอถามท่านผู้รู้หน่อยครับ..ในวงกลมสีแดงของ F 16 ทั้งสองลำทำไมไม่เหมือนกันครับ..และมันคืออะไรครับ..ขอบคุณครับ
รูปบนคือ F-16 Advanced Block 50/52+ แนวบนหลังเครื่องคือพื้นที่ระบบเอวิโอนิคส์รุ่นใหม่กว่า
ตัวล่างผมเดาว่าน่าจะเป็น Block25ครับ
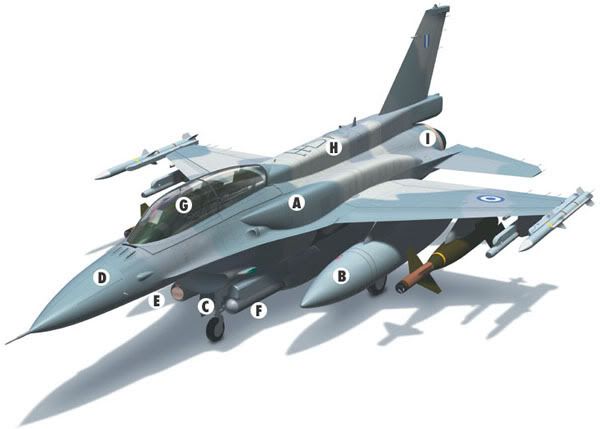

A: Conformal Fuel Tanks
The most distinguishing external feature of an Advanced Block 50/52, when installed, is a set of conformal fuel tanks attached to the upper fuselage.
All of these latest F-16s have structural, plumbing, and wiring provisions for the conformal tanks.
The tank set holds 450 gallons (more than 3,000 pounds) of additional JP-5/8.
The extra fuel increases range, loiter time, and combat persistence as well as reduces the demand for tanker support.
Range increase is on the order of twenty to forty percent, depending on the stores configuration and mission profile.
The conformals, which can be used in lieu of wing tanks, free the inner wing store stations and can double the primary air-to-ground payload.
The tanks have an imperceptible effect on the F-16's agility, handling qualities, flight limits, and signature. Moreover,
the tanks do not interfere with daily inspections and servicing, and the impact on maintenance access is minimal.
A complete set can be removed or replaced in two hours by a small crew and a hoist.
B: 600-Gallon Wing Tanks
The Advanced Block 50/52 variant is certified to carry the 600-gallon wing fuel tanks. These tanks increase range
or persistence up to thirty percent over the standard 370-gallon wing tanks. The tanks are mounted on non-jettisonable pylons
that can also carry the more common 370-gallon tanks.
C: Landing Gear
The Advanced Block 50/52 versions have heavy-weight landing gear designed for up to 52,000 pounds maximum takeoff gross weight.
D: Radar
Northrop Grumman's AN/APG-68(V)9 multimode radar will enable crews to detect airborne threats
from a range 30% greater than the existing APG-69 system and adds a synthetic-aperture radar mode for high-resolution ground mapping.
A major enhancement is the Northrop Grumman 600-gallon wing fuel tanks multimode radar, one of the most advanced radars in the skies today.
This radar has more than fivefold faster processing speed and tenfold greater memory capacity over the previous APG-68(V)7/8 radar.
The new processors have even higher growth potential.
A high-resolution synthetic aperture radar mode allows the pilot to locate and recognize tactical ground targets from considerable distances.
In conjunction with inertially aided weapons, such as GBU-31 Joint Direct Attack Munition, the AGM-154 Joint Standoff Weapon,
and CBU-103/104/105 Wind Corrected Munitions Dispenser, the F-16 gains an enhanced capability for all-weather precision strike from standoff distances.
The radar features an inertial measurement unit that improves dynamic tracking performance and provides an auto-boresight capability,
which increases accuracy and eliminates the need for time-consuming mechanical boresighting.
Air-to-air improvements in-clude a thirty percent increase in detection range and improvements in functionality and tracking quality in various modes.
Radar reliability is increased by fifty percent to nearly 400 hours mean time between failures.
Commercial off-the-shelf technology is expected to improve supportability significantly. Using off-the-shelf technology resolves existing issues with availability
and cost of spare parts and also makes technology refreshes more affordable.
E: Targeting System
The Advanced Block 50/52 can employ the latest generation targeting systems, such as the Lockheed Martin Sniper XR/Pantera targeting pod
that is mounted on the right inlet sensor station. In conjunction with laser-guided bombs, the pod provides day/night precision strikes from high altitudes.
Among other uses, the targeting systems can be used for seeker cueing of a variety of guided weapons and covert air-to-air operations.
F: Navigation and Reconnaissance Pods
A navigation pod, such as LANTIRN/Pathfinder, can be fitted to the left inlet sensor station.
A variety of reconnaissance pods can be carried on the centerline fuselage station.
G: Cockpit
The Advanced Block 50/52 cockpit features a helmet-mounted cueing system, color multifunction displays and recording equipment,
cockpit lighting and external strip lighting compatible with night vision goggles, and large-capacity data transfer sets.
A choice of helmet-mounted cueing systems is available.
These systems allow a pilot to direct sensors or weapons to his line of sight or to help him find a designated target.
The helmet display also provides critical flight and target information to the pilot similar to a head-up display, but in any direction the pilot looks.
H: Dorsal Avionics Compartment
All two-seat models of the Advanced Block 50/52 have a distinctive dorsal avionics compartment that allows these aircraft
to accommodate all of the systems of the single-seat model as well as some special mission equipment and additional chaff/flare dispensers.
The rear cockpit can be configured for either a weapon system operator or an instructor pilot and can be converted with a single switch in the cockpit.
I: Engines
The Advanced Block 50/52 aircraft have a common engine bay that allows customers a choice of engines in the 29,000-pound thrust class.
The Block 50s are powered by the General Electric F110-GE-129 and have the Modular Common Inlet Duct (known as the large mouth inlet).
The Block 52s are powered by the Pratt & Whitney F100-PW-229 and have a Normal Shock Inlet (known as the small mouth inlet).
 http://israelmilitary.net/showthread.php?t=1253
http://israelmilitary.net/showthread.php?t=1253